[JAVA의 정석]HashSet
이 글은 유튜브 '자바의 정석 - 기초편'을 보고 정리한 글입니다.
📂content
1. 순서X, 중복X
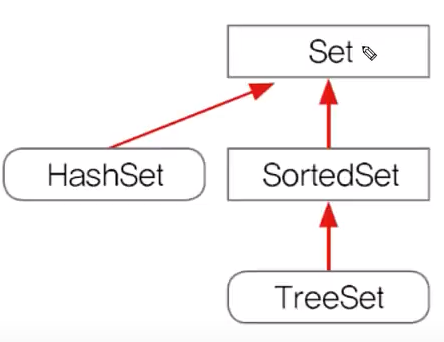
⚝ HashSet
- Set인터페이스를 구현한 대표적인 컬렉션 클래스
- 순서를 유지하려면, LinkedHashSet클래스를 사용하면 된다.
⚝ TreeSet
- 범위 검색과 정렬에 유리한 컬렉션 클래스
- (데이터가 많을수록) HashSet보다 데이터 추가, 삭제에 시간이 더 걸림
2. 주요 메서드
⚝ 생성자
HashSet()
HashSet(Collection c)
HashSet(int initialCapacity) 초기용량
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)
initialCapacity는 초기용량이다. 용량을 초과하면 보통 2배로 늘리는데 언제 늘릴 것인지 정해놓는 것이 loadFactor이다. 만약 0.8로 해놓는다면, 80% 가득 찼을 때 *2 하는 것이다.
⚝ 추가, 삭제
boolean add(Object o) : 추가
boolean addAll(Collection c) : 합집합
boolean remove(Object o) : 삭제
boolean removeAll(Collection c) : 교집합
boolean retainAll(Collection c) : 조건부 삭제(차집합)
void clear() : 모두 삭제
⚝ 그 외
boolean contains(Object o)
boolean containsAll(Collection c)
Iterator iterator()
boolean isEmpty()
int size()
Object[] toArray()
Object[] toArray(Object[] a)
⍟실습
package etc;
import java.util.*;
public class Ex11_9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object[] objArr = {"1",new Integer(1),"2","2","3","3","4","4","4"};
Set set = new HashSet();
for(int i=0; i < objArr.length; i++) {
set.add(objArr[i]); // HashSet에 objArr의 요소들을 저장한다.
}
// HashSet에 저장된 요소들을 출력한다.
System.out.println(set); //[1, 1, 2, 3, 4]
// HashSet에 저장된 요소들을 출력한다.(Iterator이용)
Iterator it = set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
/**
* 1
* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
*/
}
}
}
- 결과가 [1, 1, 2, 3, 4]로 나온다. 중복인데 왜 1이 두 번 나오지? 한다면 하나는 Integer이고 하나는 String이기 때문이다. 그런데 Set은 순서가 없기 때문에 먼저 출력된 것이 Integer이고 String인지는 알 수 없다.
package etc;
import java.util.*;
public class Ex11_10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new HashSet();
//set의 크기가 6보다 작은 동안 1~45사이의 난수를 저장
for (int i = 0; set.size() < 6 ; i++) {
int num = (int)(Math.random()*45) + 1;
// set.add(new Integer(num));
set.add(num);
}
//1. Set의 모든 요소를 List에 저장
List list = new LinkedList(set); // LinkedList(Collection c)
//2. List를 정렬
Collections.sort(list); // Collections.sort(List list)
//3. List를 출력
System.out.println(list);
}
}
3. 중복 확인
- HashSet은 객체를 저장하기 전에 기존에 같은 객체가 있는지 확인
같은 객체가 없으면 저장하고, 있으면 저장하지 않는다.
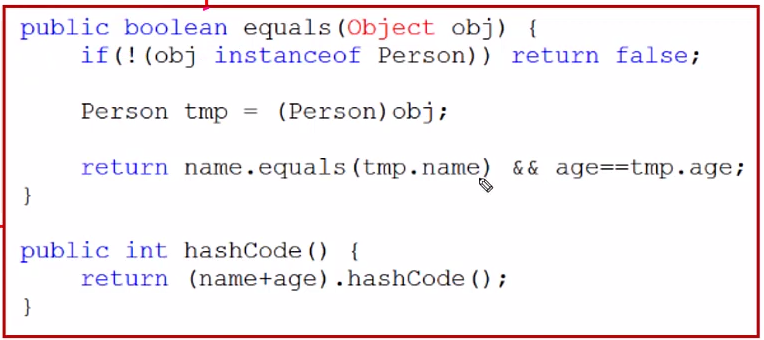
- boolean add(Object o)는 저장할 객체의 equals()와 hashCode()를 호출
equals()와 hashCode()가 오버라이딩 되어 있어야 함.
class Person {
String name;
int age;
Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return name +":"+ age;
}
}
- Person이라는 class가 있을 때 Person객체를 호출한다고 하면 equals()와 hashCode()를 호출해야 하는 것임. 그런데 이 두 메소드는 Object 클래스에 있다. 그리고 생략이 되어 있지만 Object의 상속을 받고 있다. 그래서 문제가 없다. 하지만 이 두 메소드가 오버라이딩 되어 있지 않으면 문제가 생긴다.
- 요즘은 return Objects.hash(name, age)와 같은 방식으로 오버라이딩을 해준다.
- age 앞에 사실 this가 생략됨. this와 매개변수와 비교하는 것이다.
⍟실습
package etc;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Ex11_11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet();
set.add("abc");
set.add("abc");
set.add(new Person("David",10));
set.add(new Person("David",10));
System.out.println(set);
}
}
//equals()와 hashCode()를 오버라이딩해야 HashSet이 바르게 동작.
//그렇지 않으면 출력 결과가 [David:10, abc, David:10]로 중복된 클래스도 집어넣는다.
//올바른 결과는 [David:10, abc]이다.
class Person {
String name;
int age;
@Override
public int hashCode() {
//int hash(Object... values); //가변인자 : 매개변수 마음대로
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if(!(o instanceof Person)) return false;
Person p = (Person)o;
//나 자신(this)의 이름과 나이를 p와 비교
//형변환 안 하면 Object에는 name과 age가 없어서 오류가 난다.
return this.name.equals(p.name) && this.age == p.age;
}
Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return name +":"+ age;
}
}
package etc;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Ex11_12 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
HashSet setA = new HashSet();
HashSet setB = new HashSet();
HashSet setHab = new HashSet();
HashSet setKyo = new HashSet();
HashSet setCha = new HashSet();
setA.add("1"); setA.add("2"); setA.add("3");
setA.add("4"); setA.add("5");
System.out.println("A = "+setA); //A = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
setB.add("4"); setB.add("5"); setB.add("6");
setB.add("7"); setB.add("8");
System.out.println("B = "+setB); //B = [4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
//1. 교집합
//setA.retainAll(setB); //공통된 요소만 남기고 삭제
Iterator it = setB.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Object tmp = it.next();
if(setA.contains(tmp))
setKyo.add(tmp);
}
//2. 차집합
//setA.removeAll(setB); //setB와 공통 요소를 제거
it = setA.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Object tmp = it.next();
if(!setB.contains(tmp))
setCha.add(tmp);
}
//3. 합집합
//setA.addAll(setB); //setB의 모든 요소를 추가(중복 제외)
it = setA.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
setHab.add(it.next());
it = setB.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
setHab.add(it.next());
//결과 출력
//A ∩ B = [4, 5]
System.out.println("A ∩ B = " + setKyo); // 한글 ㄷ을 누르고 한자키
//A U B = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
System.out.println("A U B = " + setHab); // 한글 ㄷ을 누르고 한자키
//A - B = [1, 2, 3]
System.out.println("A - B = " + setCha);
}
}
출처